Key Points
Low blood sugar and high insulin level is usually associated with an insulinoma
Surgical removal of the tumor frequently will extend the life of the patient but the prognosis is guarded as the tumor commonly metastasizes
Medical therapy is commonly needed to control signs of low blood sugar
Anatomy
The pancreas in dogs and cats have a left lobe, right lobe and body. The body contains ducts (channels) that connect to the small intestine. The pancreas has two major functional components: the exocrine pancreas and the endocrine pancreas. The exocrine pancreas is glandular tissue that secretes digestive enzymes into the intestine; these enzymes digest food. The endocrine pancreas is located in nests of tissue called the ilets of Langerhan. These produce a number of chemical messengers including insulin that are secreted directly into the blood stream. Insulin secretion is regulated by the blood sugar level; thus, when the sugar level is high insulin is secreted, but when the sugar level is low, insulin secretion is stopped.
Insulinoma
This type of tumor originates from the beta cells of the ilets of Langerhan and secrete uncontrolled amounts of insulin. These tumors are always malignant and invarialby spread to regional lymph nodes, liver and sometimes to the lungs
Signs
Predisposed breeds include Irish Setters, Golden Retriever, German Shepernds, Boxers and Standard Poodles; average age of affected dogs is about 9 to 10 years of age. Clinical signs are primarily due to low blood sugar and these include seizures, collapse, weakness, hindlimb weakness, depression, wobbliness when walking, muscle twitching, abnormal behavior, increased appetite, intolerance to exercise, shaking, weight gain, head tilt, head jerking, facial twitching, diarrhea, disorientation, episodes of blindness, hyperactivity and in some cases no clinical signs.
Diagnosis
A low blood sugar and a high insulin level in the blood are classic findings in a patient with insulinoma. Because the blood sugar level will fluctuate in patients with an insulinoma, it is important to measure the blood insulin levels when the blood sugar level is less than 60 mg/dl. Abdominal ultrasound may or may not show the mass within the pancreas, as this is dependant on the size of the tumor. In addition, lymph nodes, liver and other internal organs are imaged for evidence of gross metastatic disease. Chest x-rays rarely demonstrate spread of tumor to the lungs. Nuclear scintigraphy with radiolabled octreotide is sensitive to identify very small tumors.
Day of surgery
The anesthesia and surgical team will prescribe a pain management program, both during and after surgery that will keep your companion comfortable. This may include a combination of general anesthesia, injectable analgesics, and oral analgesics.
Control of low blood sugar prior to surgery includes frequent meals, with a diet containing high protein and low sugar content. Prednisone, a corticosteroid, can be given to increase the blood sugar level. Side effects from this medication may include increased thrist, increased urination, increased appetite, restlessness behavioral changes, and weight gain. Diazoxide can also be prescribed to increase the blood sugar. Side effects include anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea. These side effects can be minimized by reducing the dose and giving the medication with food. None of these medical therapies have any anti-cancer effect.
If a pet is found to be seizuring or comatosed at home, corn syrup can be put under the tongue to help increase the blood sugar level. You should seek immediate medical attention for your pet. At a veterinary hospital, a continual infusion of glucogon through an intravenous line is administered to for emergent control of low blood sugar. Intravenous dextrose (sugar) may also be required if the patient has severe neurological signs.
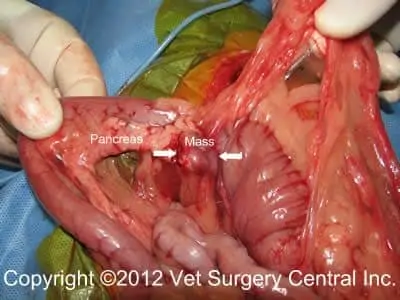
An incision is made into the abdomen to allow the surgeon to examine of the internal organs. A section of the pancreas with its associated tumor is removed. If the mass is located in the body of the pancreas, close to the important pancreatic ducts, the mass is gently dissected from the pancreatic tissue. These tumors may be small and difficult to see. A dye called new methylene blue can be administered to the patient to assist in identification of the mass.
Complications following surgery may include inflamation of the pancreas, continued low blood sugar or diabetes mellitus.
Aftercare
An analgesic medication may be required once the pet goes home. If the blood sugar returns to normal after surgery, a regular diet can be be fed. If the blood sugar still mildly decreased after surgery, a high protein diet with low carbohydrate content should be fed. In some cases, prednisone may still be needed. If the patient has too high of blood sugar, insulin may be needed for a short period of time.
Prognosis
Surgery does not cure patients with insulinoma, rather will help with clinical signs of low blood sugar for a period of time. Survival times with stage 1 tumors (isolated only to the pancreas) is 20 months with recurrence of hypoglycemia at 17 months. Survival time for stage 2 tumors (in the pancreas and the regional lymph nodes) is 10 months with recurrence of hypoglycemia at 2 months postop. Survival time for stage 3 tumors (in pancras, regional lymph nodes, and liver) is 6 months with recurrence of hypoglycemia at 1 to 2 months postop.


