Stroke clinical signs
Brain stroke is uncommon in dogs and can result in a variety of neurological manifestations.
Here is an example of a dog that had an acute stroke in the left thalamic region of the brain. The primary sign was circling to the left. His attitude was somewhat dull.
Diagnostics
MRI scan was completed with contrast is the test of choice to diagnose a stroke in a dog. The scan may show an area of hemorrhage of infarction. The example below in Rudy (as seen in the video) shows a small area deep within the brain that has an increased signal. This lesion is not a tumor, as these typically get very bright on a contrast T1 study (see images below)
MRI fast stir
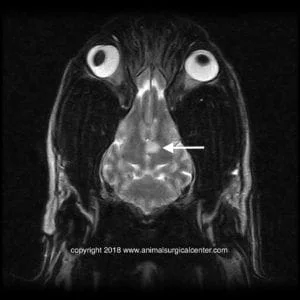
T2 dorsal view
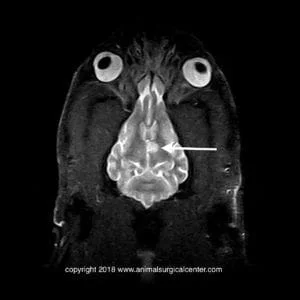
Dorsal stir – left thalamic lesion
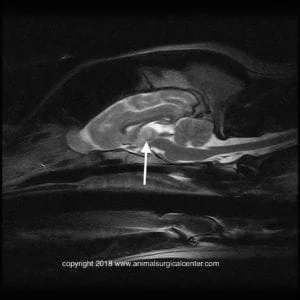
T2 sagittal view – lesion in thalamic region
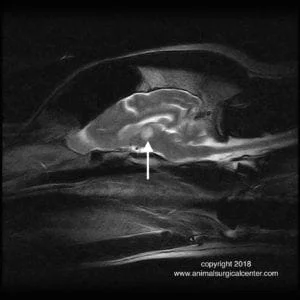
T2 sagittal view showing thalamic lesion
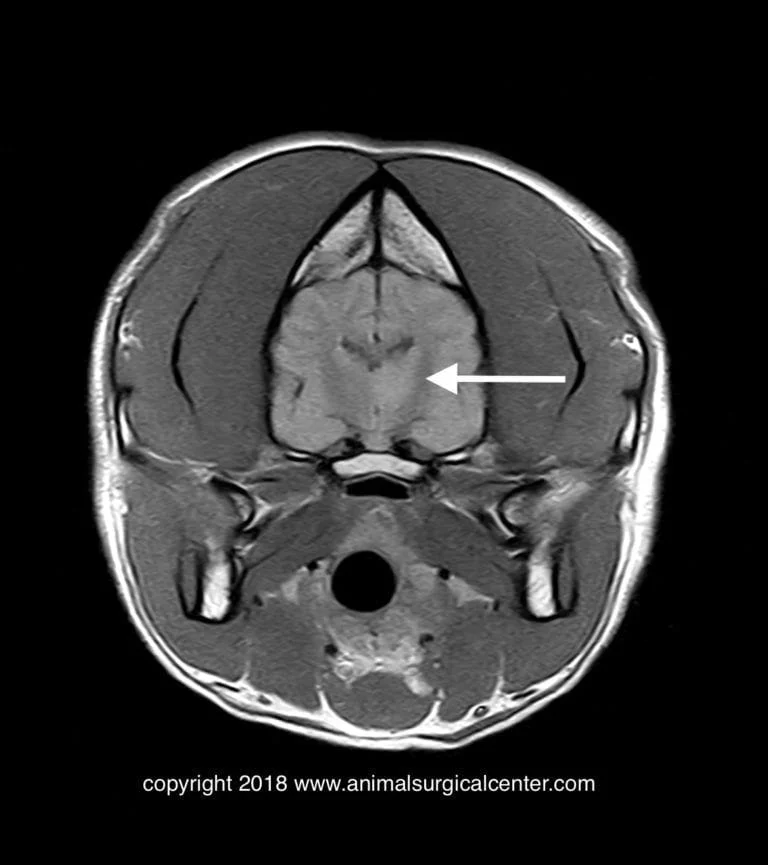
T1 precontrast – note hyperintense lesion seen in the interthalamic region
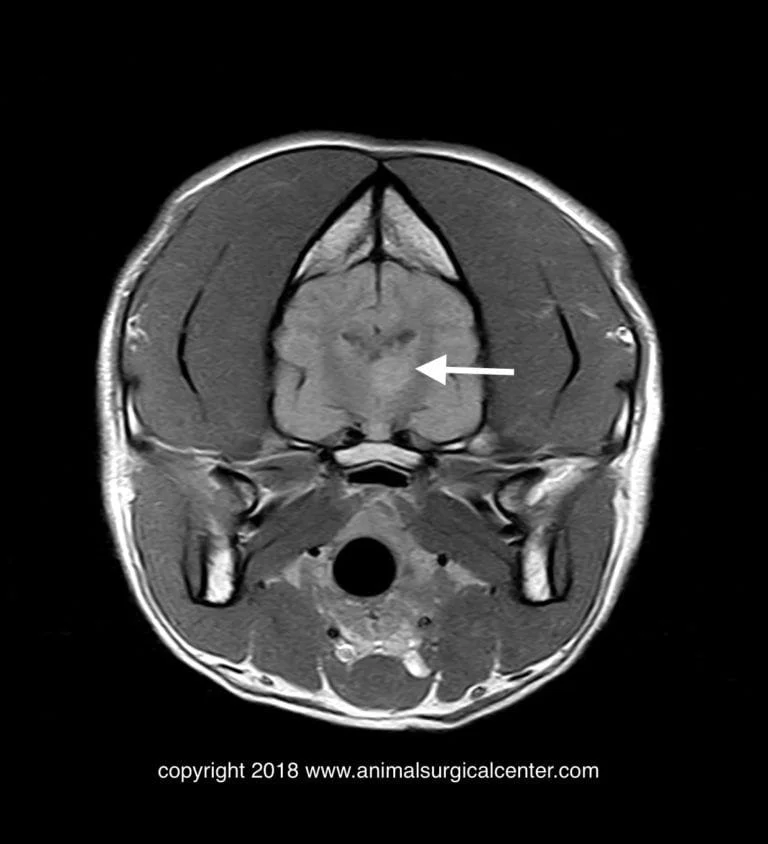
T1 – post gadolinium contrast. The lack of enhancement is indicative of a stroke in this dog.
Treatment
No specific treatment was needed for this patient. Blood pressure should be measured and if hypertension is noted, anti-hypertensive medication (typically amlodipine) should be prescribed.
In this patient you can see that only after 2 weeks he has returned to normal neurological function.
Prognosis
Patient that are not severely affected by a stroke have an excellent prognosis. Severely affected patients may not regain normal function.


